If you want to know about “kali linux”. So, your search ends here. Here you find all aspects about kali linux. If you want to know about Digital Marketing. So, “click here“.
Table of Contents

Introduction About Kali Linux
Kali Linux is a powerful and widely-used operating system designed for digital forensics, penetration testing, and security auditing. It is renowned for its vast array of pre-installed tools specifically crafted for ethical hacking and cybersecurity tasks. Originally developed from the foundations of Debian Linux, Kali has evolved into a specialized distribution tailored for professionals and enthusiasts in the field of cybersecurity.
One of Kali Linux’s primary strengths lies in its comprehensive suite of penetration testing tools, which cover various aspects of cybersecurity assessment, including network analysis, vulnerability assessment, exploitation, and forensics. These tools are meticulously organized and regularly updated to ensure compatibility and effectiveness in identifying and addressing security vulnerabilities.
Define Kali Linux
Kali Linux is an open-source operating system specifically designed for digital forensics, penetration testing, and cybersecurity tasks. It provides a comprehensive array of pre-installed tools and utilities tailored for ethical hacking and security auditing purposes. Kali Linux is widely used by cybersecurity professionals, researchers, and enthusiasts to assess and strengthen the security of systems and networks.
Benifits of Kali Linux
Pre-installed Tools: Kali Linux comes with a vast array of pre-installed tools for penetration testing, digital forensics, and security auditing, saving users time and effort in manually installing them.
Specialized Distribution: It is specifically tailored for cybersecurity professionals and enthusiasts, offering a focused environment with tools and utilities optimized for ethical hacking and security assessments.
Regular Updates: Kali Linux receives regular updates to its tools and packages, ensuring users have access to the latest security vulnerabilities, exploits, and techniques for testing and fortifying systems.
Community Support: With a large and active community of users and developers, Kali Linux offers robust support through forums, documentation, and online resources, making it easier for users to troubleshoot issues and share knowledge.
Flexibility and Customization: Kali Linux provides a flexible platform that allows users to customize their environments according to their specific needs and preferences, enabling tailored workflows and configurations.
Educational Resource: It serves as an invaluable educational resource for learning about cybersecurity concepts, techniques, and methodologies, offering hands-on experience with real-world tools and scenarios.
Legal and Ethical Use: Kali Linux promotes legal and ethical hacking practices, encouraging users to utilize its tools responsibly and within the bounds of applicable laws and regulations.
Compatibility and Portability: Being based on Debian Linux, Kali Linux offers compatibility with a wide range of hardware and software systems, while its live USB and virtual machine support enhance portability and ease of use.
Dis-Advantages of Kali Linux
Steep Learning Curve: Kali Linux can be challenging for beginners due to its specialized focus on cybersecurity and the complexity of its tools. Users may require significant time and effort to become proficient in using its features effectively.
Potential Misuse: While Kali Linux is intended for ethical hacking and security testing purposes, there is a risk of misuse by individuals with malicious intent. Improper use of the tools included in Kali Linux can lead to legal and ethical consequences.
Resource Intensive: Some of the tools and utilities included in Kali Linux can be resource-intensive, requiring substantial processing power, memory, and storage. Users with older or less powerful hardware may experience performance issues.
Limited Non-Security Features: Kali Linux prioritizes security tools over general-purpose software, which means it may lack certain non-security-related features and applications commonly found in other Linux distributions. This can be a limitation for users who require a more versatile operating system.
Potential for System Instability: As with any specialized operating system, Kali Linux may be more prone to system instability or compatibility issues, particularly when using bleeding-edge or experimental tools and packages.
Tools of Kali Linux

Information Gathering: Tools designed to gather information about target systems, networks, and vulnerabilities, such as Nmap, Recon-ng, and Maltego.
Vulnerability Analysis: Tools used to identify and assess vulnerabilities in target systems, including OpenVAS, Nikto, and Nexpose.
Exploitation: Tools utilized to exploit identified vulnerabilities and gain unauthorized access to systems, such as Metasploit Framework, BeEF, and ExploitDB.
Password Attacks: Utilities for performing password cracking and authentication bypass techniques, including John the Ripper, Hydra, and THC-Hydra.
Wireless Attacks: Tools focused on conducting attacks against wireless networks and devices, such as Aircrack-ng, Reaver, and Wireshark.
Forensics: Software for digital forensics and incident response activities, including Autopsy, Foremost, and Volatility Framework.
Reverse Engineering: Tools used to analyze and reverse engineer software and malware, such as Radare2, IDA Pro, and Ghidra.
Web Application Testing: Utilities for testing the security of web applications, including Burp Suite, OWASP ZAP, and SQLMap.
Social Engineering: Tools for performing social engineering attacks and manipulation techniques, such as SET (Social-Engineer Toolkit) and BeEF.
Stress Testing: Utilities for conducting stress tests and assessing the resilience of systems under load, including Apache JMeter and Siege.

How to install Kali Linux Step By Step
Download Kali Linux ISO: Go to the official Kali Linux website and download the ISO image of the latest version compatible with your system architecture (32-bit or 64-bit).
Create Bootable Media: Once the ISO file is downloaded, you can create a bootable USB drive or DVD using software like Rufus (for Windows) or Etcher (for Linux and macOS).
Boot from Installation Media: Insert the bootable USB drive or DVD into your computer and restart it. Access the boot menu or BIOS settings (usually by pressing F2, F10, or Del during startup) to select the boot device as the USB drive or DVD.
Start Installation: After booting from the installation media, you’ll see the Kali Linux boot menu. Select the “Graphical Install” option to begin the installation process.
Choose Language: Select your preferred language for the installation process and click “Continue.”
Select Location: Choose your location from the list provided and click “Continue.”
Configure Keyboard: Select the appropriate keyboard layout for your system and click “Continue.”
Setup Network: If your system requires network configuration, enter the hostname for your system and select a domain name. Then, configure the network manually or use DHCP. Click “Continue” when done.
Set Up Disk Partitioning: Choose the disk on which you want to install Kali Linux. You can select the guided partitioning option for automatic partitioning or manually partition the disk according to your preferences. Click “Continue” when ready.
Confirm Partition Changes: Review and confirm the changes to disk partitions. Select “Finish partitioning and write changes to disk” and click “Continue” to proceed.
Install GRUB Boot Loader: Choose the device where you want to install the GRUB boot loader (usually the default option is the correct one). Click “Continue.”
Complete Installation: Wait for the installation process to complete. Once finished, you’ll be prompted to remove the installation media and restart your computer.
Login: After rebooting, you’ll see the Kali Linux login screen. Enter the username and password you created during the installation process.
Update and Customize: After logging in, it’s recommended to update your system packages and customize your Kali Linux environment according to your preferences.
Commands Of Kali Linux
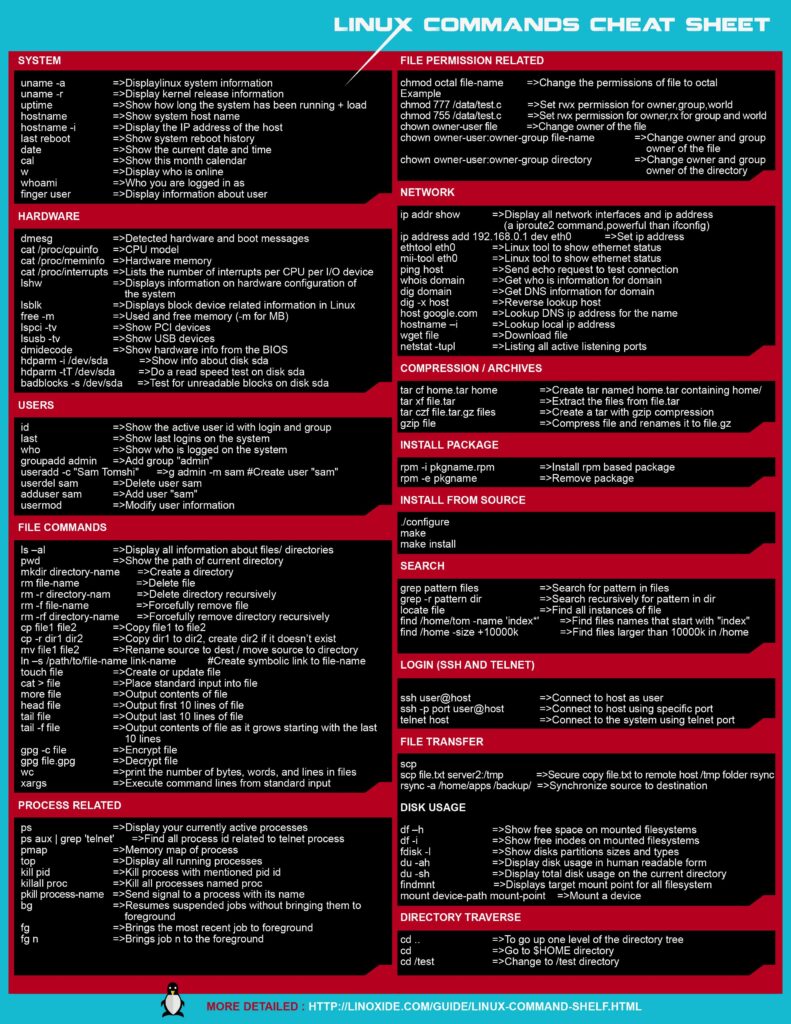
Navigation Commands:
- pwd: Display the current working directory.
- ls: List files and directories in the current directory.
- cd: Change directory.
- Example:
cd Documents(change to the Documents directory).
- Example:
- mkdir: Create a new directory.
- Example:
mkdir new_folder(create a directory named “new_folder”).
- Example:
- rmdir: Remove an empty directory.
- Example:
rmdir old_folder(remove the directory named “old_folder”).
- Example:
File Management Commands:
- touch: Create a new empty file or update the timestamp of an existing file.
- Example:
touch file.txt(create a file named “file.txt”).
- Example:
- cp: Copy files or directories.
- Example:
cp source_file destination_directory(copy a file to a destination directory).
- Example:
- mv: Move or rename files or directories.
- Example:
mv old_file new_file(rename a file).
- Example:
- rm: Remove files or directories.
- Example:
rm unwanted_file(remove a file). - Note: Use with caution, as it permanently deletes files.
- Example:
Text Editing Commands:
- nano: Open the Nano text editor.
- Example:
nano filename(open or create a file named “filename”).
- Example:
- vi or vim: Open the Vim text editor.
- Example:
vi filename(open or create a file named “filename”). - Note: Vim has different modes (insert mode, command mode, etc.). Press
ito enter insert mode, make changes, then pressEscand:wqto save and exit.
- Example:
System Information Commands:
- uname: Display system information.
- Example:
uname -a(display all system information).
- Example:
- top: Display real-time system information, including CPU and memory usage.
- Example:
top(display system processes).
- Example:
- df: Display disk space usage.
- Example:
df -h(display disk space in human-readable format).
- Example:
Network Commands:
- ifconfig or ip: Display network interface information.
- Example:
ifconfigorip addr(display network interfaces).
- Example:
- ping: Send ICMP echo requests to a host.
- Example:
ping google.com(ping Google’s server).
- Example:
Package Management Commands (for Debian/Ubuntu):
- apt: Package management tool for installing, updating, and removing packages.
- Example:
sudo apt update(update package lists). - Example:
sudo apt install package_name(install a package). - Example:
sudo apt remove package_name(remove a package).
- Example:
Process Management Commands:
- ps: Display information about running processes.
- Example:
ps aux(display all running processes).
- Example:
- kill: Terminate a process by its ID.
- Example:
kill process_id(terminate a process).
- Example:
File Permissions Commands:
- chmod: Change file permissions.
- Example:
chmod +x script.sh(grant execute permission to a script).
- Example:
- chown: Change file ownership.
- Example:
chown user:group filename(change file ownership).
- Example:
Conclusion
In conclusion, Kali Linux stands as a pivotal tool in the arsenal of cybersecurity professionals, enthusiasts, and ethical hackers alike. With its comprehensive suite of pre-installed tools and utilities tailored for digital forensics, penetration testing, and security auditing, Kali Linux provides a powerful platform for assessing and fortifying the security posture of systems and networks.
Check our other articles“”

Nice 👌
Thank you ✌️ and check our other blogs.